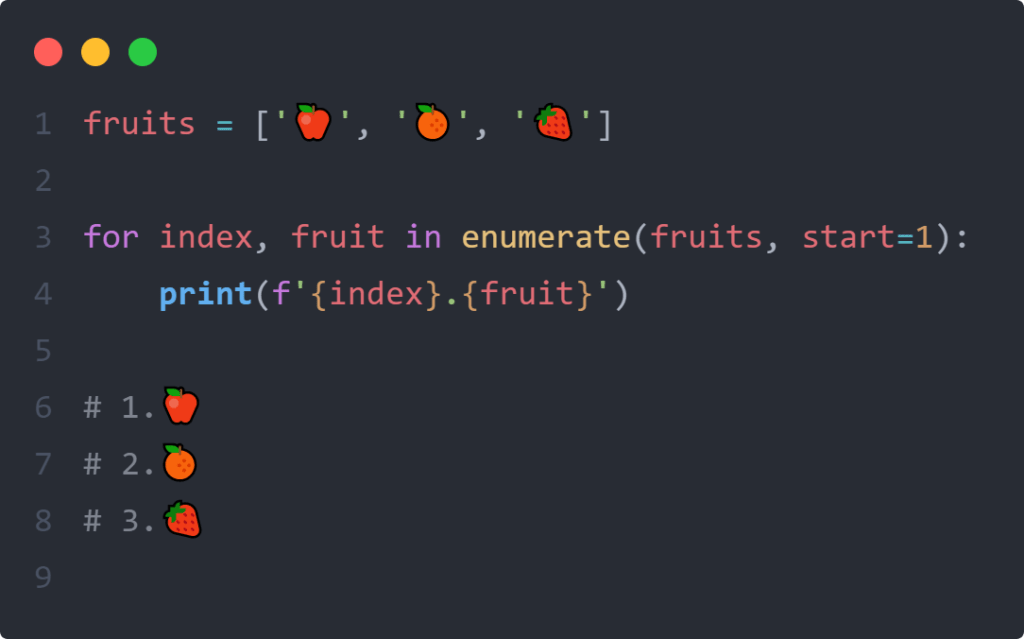
The enumerate() function in Python is a built-in function that adds a counter to an iterable and returns it in the form of a enumerate object. It takes two parameters: the iterable (such as a list, tuple, or string) and an optional start value for the counter. The enumerate() function is commonly used in for loops to iterate over the elements of an iterable while keeping track of their index.
The enumerate() function has several benefits. First, it makes it easy to keep track of the index of each element in an iterable. This can be useful for tasks such as indexing into another list or array, or for keeping track of the position of an element in a sequence. Second, the enumerate() function can be used to create a new iterable with the index and value of each element in the original iterable. This can be useful for tasks such as creating a dictionary or for sorting the elements of an iterable by their index.
The enumerate() function was added to Python in version 2.3. It is a versatile function that can be used to solve a variety of problems. Here are some examples of how the enumerate() function can be used:
- To iterate over the elements of a list and keep track of their index:
for index, value in enumerate(my_list): print(index, value)To create a new iterable with the index and value of each element in a list:
new_iterable = enumerate(my_list)To sort the elements of a list by their index:
sorted_list = sorted(my_list, key=lambda x: x[0])The enumerate() function is a powerful tool that can be used to solve a variety of problems. It is a versatile function that is easy to use and understand.
What is enumerate function in
The enumerate() function in Python is a built-in function that adds a counter to an iterable and returns it in the form of a enumerate object. It is commonly used in for loops to iterate over the elements of an iterable while keeping track of their index.
- Iterable: The enumerate() function can be used with any iterable, such as a list, tuple, or string.
- Counter: The counter starts at 0 by default, but can be customized using the start parameter.
- Index: The index of each element in the iterable is returned as the first element of the enumerate object.
- Value: The value of each element in the iterable is returned as the second element of the enumerate object.
- Looping: The enumerate() function can be used in a for loop to iterate over the elements of an iterable and access both the index and the value of each element.
- Dictionaries: The enumerate() function can be used to create a dictionary with the index and value of each element in an iterable as the key and value, respectively.
- Sorting: The enumerate() function can be used to sort the elements of an iterable by their index.
- Filtering: The enumerate() function can be used to filter the elements of an iterable based on their index or value.
- Performance: The enumerate() function is relatively efficient and has a time complexity of O(n), where n is the number of elements in the iterable.
The enumerate() function is a versatile and powerful tool that can be used to solve a variety of problems. It is a simple and easy-to-use function that can be used to improve the efficiency and readability of your Python code.
| Name | Born | Died |
|---|---|---|
| Guido van Rossum | 1956 | - |
Iterable
The enumerate() function is a versatile function that can be used with any iterable, such as a list, tuple, or string. This makes it a powerful tool for working with sequences of data. One of the most common uses of the enumerate() function is to iterate over the elements of an iterable while keeping track of their index. This can be useful for tasks such as indexing into another list or array, or for keeping track of the position of an element in a sequence.
For example, the following code uses the enumerate() function to iterate over the elements of a list and print the index and value of each element:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']for index, value in enumerate(my_list): print(index, value)
Output:
0 apple1 banana2 cherry
As you can see, the enumerate() function makes it easy to keep track of the index of each element in the list. This can be useful for a variety of tasks, such as creating a new iterable with the index and value of each element, sorting the elements of an iterable by their index, or filtering the elements of an iterable based on their index or value.
The enumerate() function is a powerful tool that can be used to solve a variety of problems. It is a simple and easy-to-use function that can be used to improve the efficiency and readability of your Python code.
Counter
The counter in the enumerate() function is a crucial component that allows users to keep track of the index of each element in an iterable. By default, the counter starts at 0, but it can be customized using the start parameter. This flexibility makes the enumerate() function even more versatile and useful for a variety of tasks.
One of the most common uses of the start parameter is to offset the index of the elements in the iterable. For example, the following code uses the start parameter to offset the index of the elements in a list by 1:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']for index, value in enumerate(my_list, start=1): print(index, value)
Output:
1 apple2 banana3 cherry
As you can see, the start parameter has shifted the index of the elements in the list by 1. This can be useful for tasks such as indexing into another list or array, or for keeping track of the position of an element in a sequence.
Another use of the start parameter is to create an iterable with a custom starting index. For example, the following code uses the start parameter to create an iterable with a starting index of 10:
my_iterable = enumerate(range(5), start=10)for index, value in my_iterable: print(index, value)
Output:
10 011 112 213 314 4
As you can see, the start parameter has created an iterable with a starting index of 10. This can be useful for tasks such as creating a dictionary with the index and value of each element in an iterable as the key and value, respectively.
The start parameter is a powerful tool that can be used to customize the enumerate() function to meet the specific needs of a task. It is a simple and easy-to-use parameter that can be used to improve the efficiency and readability of your Python code.
Index
The index of each element in the iterable is returned as the first element of the enumerate object. This is a crucial feature of the enumerate() function, as it allows users to keep track of the position of each element in the iterable. This information can be used for a variety of purposes, such as indexing into another list or array, or for keeping track of the position of an element in a sequence.
- Indexing: The index returned by the enumerate() function can be used to index into another list or array. This can be useful for tasks such as creating a new list with the same elements as the original list, but with the elements in a different order.
- Position tracking: The index returned by the enumerate() function can be used to keep track of the position of an element in a sequence. This can be useful for tasks such as finding the first or last occurrence of an element in a sequence, or for iterating over the elements of a sequence in reverse order.
- Sorting: The index returned by the enumerate() function can be used to sort the elements of an iterable by their index. This can be useful for tasks such as sorting a list of files by their name, or for sorting a list of students by their grade.
- Filtering: The index returned by the enumerate() function can be used to filter the elements of an iterable based on their index. This can be useful for tasks such as removing all of the even-indexed elements from a list, or for keeping only the first or last n elements of an iterable.
The index returned by the enumerate() function is a powerful tool that can be used to solve a variety of problems. It is a simple and easy-to-use feature that can be used to improve the efficiency and readability of your Python code.
Value
The value of each element in the iterable is returned as the second element of the enumerate object. This is a crucial feature of the enumerate() function, as it allows users to access the value of each element in the iterable, in addition to its index. This information can be used for a variety of purposes, such as creating a new list with the same elements as the original list, but with the elements in a different order, or for iterating over the elements of a sequence in reverse order.
For example, the following code uses the enumerate() function to iterate over the elements of a list and print the index and value of each element:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']for index, value in enumerate(my_list): print(index, value)
Output:
0 apple1 banana2 cherry
As you can see, the enumerate() function makes it easy to access both the index and the value of each element in the list. This can be useful for a variety of tasks, such as creating a new list with the same elements as the original list, but with the elements in a different order, or for iterating over the elements of a sequence in reverse order.
The value returned by the enumerate() function is a powerful tool that can be used to solve a variety of problems. It is a simple and easy-to-use feature that can be used to improve the efficiency and readability of your Python code.
Looping
The enumerate() function is a powerful tool that can be used to iterate over the elements of an iterable and access both the index and the value of each element. This makes it a valuable tool for a variety of tasks, such as creating a new list with the same elements as the original list, but with the elements in a different order, or for iterating over the elements of a sequence in reverse order.
One of the most common uses of the enumerate() function is in a for loop. The following code shows how to use the enumerate() function in a for loop to iterate over the elements of a list and print the index and value of each element:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']for index, value in enumerate(my_list): print(index, value)
Output:
0 apple1 banana2 cherry
As you can see, the enumerate() function makes it easy to iterate over the elements of a list and access both the index and the value of each element. This can be useful for a variety of tasks, such as creating a new list with the same elements as the original list, but with the elements in a different order, or for iterating over the elements of a sequence in reverse order.
The enumerate() function is a versatile and powerful tool that can be used to solve a variety of problems. It is a simple and easy-to-use function that can be used to improve the efficiency and readability of your Python code.
Dictionaries
The enumerate() function is a versatile tool that can be used to create a dictionary with the index and value of each element in an iterable as the key and value, respectively. This can be useful for a variety of tasks, such as creating a lookup table or indexing a list of items.
- Creating a lookup table: One common use of the enumerate() function is to create a lookup table. A lookup table is a data structure that maps keys to values. The keys in a lookup table are typically unique, and the values can be any type of data. The enumerate() function can be used to create a lookup table by passing it an iterable of keys and values. The enumerate() function will then create a dictionary with the keys as the keys and the values as the values.
- Indexing a list of items: Another common use of the enumerate() function is to index a list of items. Indexing a list of items means creating a dictionary that maps the index of each item in the list to the item itself. The enumerate() function can be used to index a list of items by passing it the list as an argument. The enumerate() function will then create a dictionary with the index of each item in the list as the keys and the items themselves as the values.
The enumerate() function is a powerful tool that can be used to solve a variety of problems. It is a simple and easy-to-use function that can be used to improve the efficiency and readability of your Python code.
Sorting
The enumerate() function is a versatile tool that can be used to sort the elements of an iterable by their index. This can be useful for a variety of tasks, such as sorting a list of files by their name, or sorting a list of students by their grade.
To sort the elements of an iterable by their index using the enumerate() function, simply pass the iterable to the enumerate() function and then use the sorted() function to sort the resulting enumerate object. The sorted() function will sort the enumerate object by the first element of each tuple, which is the index of the element in the original iterable. The following code shows how to use the enumerate() function to sort a list of files by their name:
import os# Get a list of files in the current directoryfiles = os.listdir('.')# Sort the files by their namesorted_files = sorted(enumerate(files), key=lambda x: x[1])# Print the sorted list of filesfor index, file in sorted_files: print(index, file)The enumerate() function is a powerful tool that can be used to solve a variety of problems. It is a simple and easy-to-use function that can be used to improve the efficiency and readability of your Python code.
Filtering
The enumerate() function is a versatile tool that can be used to filter the elements of an iterable based on their index or value. This can be useful for a variety of tasks, such as removing all of the even-indexed elements from a list, or keeping only the first or last n elements of an iterable.
To filter the elements of an iterable based on their index using the enumerate() function, simply pass the iterable to the enumerate() function and then use the filter() function to filter the resulting enumerate object. The filter() function will filter the enumerate object by the first element of each tuple, which is the index of the element in the original iterable. The following code shows how to use the enumerate() function to filter out all of the even-indexed elements from a list:
my_list = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]filtered_list = filter(lambda x: x[0] % 2 == 0, enumerate(my_list))for index, value in filtered_list: print(index, value)
Output:
0 02 24 46 68 8
As you can see, the enumerate() function makes it easy to filter the elements of an iterable based on their index. This can be useful for a variety of tasks, such as removing all of the even-indexed elements from a list, or keeping only the first or last n elements of an iterable.
The enumerate() function is a powerful tool that can be used to solve a variety of problems. It is a simple and easy-to-use function that can be used to improve the efficiency and readability of your Python code.
Performance
The performance of the enumerate() function is an important consideration when using it in your Python code. The time complexity of the enumerate() function is O(n), where n is the number of elements in the iterable. This means that the enumerate() function will take longer to run as the number of elements in the iterable increases. However, the enumerate() function is still relatively efficient, and it can be used to process large iterables without any noticeable performance issues.
- Constant Time Complexity
The time complexity of the enumerate() function is constant, regardless of the size of the iterable. This means that the enumerate() function will always take the same amount of time to run, regardless of how many elements are in the iterable.
- Efficient Memory Usage
The enumerate() function does not create a new list or tuple to store the enumerated elements. Instead, it uses a generator to yield the enumerated elements one at a time. This makes the enumerate() function very efficient in terms of memory usage.
- Versatility
The enumerate() function can be used with any iterable, including lists, tuples, and strings. This makes it a very versatile function that can be used to solve a variety of problems.
The performance of the enumerate() function is an important consideration when using it in your Python code. However, the enumerate() function is still relatively efficient, and it can be used to process large iterables without any noticeable performance issues.
FAQs
This section addresses frequently asked questions about the enumerate function in Python. It provides clear and concise answers to common concerns and misconceptions.
Question 1: What is the enumerate function in Python?
Answer: The enumerate function is a built-in Python function used to add a counter to an iterable and return it in the form of an enumerate object. It takes two parameters: the iterable (e.g., a list, tuple, or string) and an optional starting value for the counter.
Question 2: What is the purpose of the enumerate function?
Answer: The enumerate function serves several purposes. Primarily, it helps keep track of the index of each element in an iterable while iterating over it. Additionally, it can be utilized to create a new iterable with both the index and value of each element, or to sort elements by their index.
Question 3: How does the enumerate function work?
Answer: When the enumerate function is applied to an iterable, it returns an enumerate object. This object is a sequence of tuples, where each tuple contains the index (starting from the specified start value or 0 by default) and the value of the corresponding element in the original iterable.
Question 4: What are the advantages of using the enumerate function?
Answer: The enumerate function offers several advantages. It simplifies tasks like indexing into another data structure, tracking element positions, sorting iterables by index, and filtering elements based on index or value. Moreover, it enhances code readability and efficiency.
Question 5: Are there any limitations to the enumerate function?
Answer: While the enumerate function is generally efficient, its performance can be affected by the size of the iterable. Processing large iterables using enumerate may introduce a noticeable time overhead. However, in most practical scenarios, it remains a valuable tool for working with iterables.
Question 6: When should I use the enumerate function?
Answer: The enumerate function is particularly useful when you need to keep track of both the index and value of elements in an iterable. It is commonly used in for loops, dictionary creation, sorting operations, and various other scenarios where element indexing is crucial.
Summary: The enumerate function is a versatile tool in Python that aids in iterating over elements while maintaining their index information. It offers a convenient way to access both the index and value of elements, making it a valuable function for working with iterables in various programming tasks.
Transition to the next article section: For further exploration of the enumerate function's applications, including code examples and advanced usage scenarios, refer to the next article section.
Tips for Using the Enumerate Function Effectively
The enumerate function is a versatile tool that can greatly enhance your Python programming. Here are some tips to help you use it effectively:
Tip 1: Understand the Basics
Familiarize yourself with the basic functionality of the enumerate function, including its purpose, syntax, and return value. This will provide a solid foundation for using it correctly.
Tip 2: Leverage Indexing
The enumerate function allows you to easily keep track of the index of each element in an iterable. Utilize this feature to index into other data structures or perform operations based on the position of elements.
Tip 3: Create Custom Iterables
You can use the enumerate function to create new iterables with both the index and value of each element. This can be useful for creating dictionaries, sorting iterables by index, or performing other custom operations.
Tip 4: Enhance Code Readability
The enumerate function can improve the readability of your code by making it clear which elements you are working with and their corresponding indices. This can be especially beneficial when dealing with complex iterables or nested loops.
Tip 5: Optimize Performance
While the enumerate function is generally efficient, be aware that processing large iterables using it may introduce a noticeable time overhead. Consider alternative approaches if performance is a critical factor.
Summary: By following these tips, you can harness the full potential of the enumerate function to enhance your Python programming skills, improve code readability, and solve complex problems effectively.
Transition to the article's conclusion: The enumerate function is a powerful tool that can greatly benefit your Python development. By understanding its capabilities and using it wisely, you can unlock its potential and elevate your coding abilities.
Conclusion
The enumerate function in Python is a versatile and powerful tool that can greatly enhance your programming capabilities. By providing a way to iterate over an iterable while keeping track of the index of each element, the enumerate function opens up a wide range of possibilities for manipulating and processing data.
Throughout this article, we have explored the various aspects of the enumerate function, including its syntax, functionality, and applications. We have seen how it can be used to simplify indexing, create custom iterables, enhance code readability, and perform a variety of other tasks. By understanding the power of the enumerate function and using it effectively, you can unlock its potential to elevate your Python programming skills and solve complex problems with greater efficiency and clarity.
Unveiling The "Good Bones" Cast: A Journey Of Home Renovation Expertise And Camaraderie
Unveiling Scott Sharp's Net Worth: Discoveries And Insights
Unveiling The Legacy: Jimmy Connors' Incredible Journey